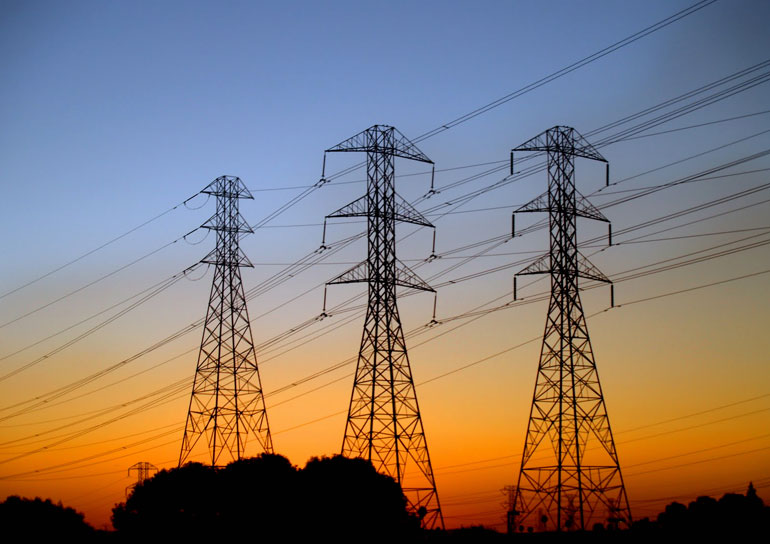
Transmission Line / Substation
Our Services
Transmission Line / Substation
This article is about the radio-frequency transmission line. For the power transmission line, see electric power transmission. For acoustic transmission lines, used in some loudspeaker designs, see acoustic transmission line.
In communications and electronic engineering, a transmission line is a specialized cable or other structure designed to carry alternating current of radio frequency, that is, currents with a frequency high enough that their wave nature must be taken into account. Transmission lines are used for purposes such as connecting radio transmitters and receivers with their antennas, distributing cable television signals, trunklines routing calls between telephone switching centres, computer network connections and high speed computer data buses.
This article covers two-conductor transmission line such as parallel line (ladder line), coaxial cable, stripline, and microstrip. Some sources also refer to waveguide, dielectric waveguide, and even optical fibre as transmission line, however these lines require different analytical techniques and so are not covered by this article; see Waveguide (electromagnetism).