Power Plants
Our Services
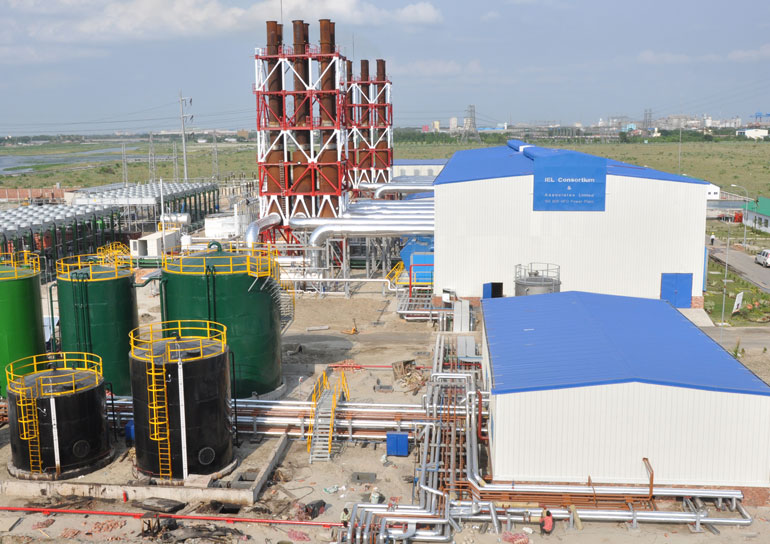
Power Plants
A power station (also referred to as a generating station, power plant, powerhouse, or generating plant) is an industrial facility for the generation of electric power. Most power stations contain one or more generators, a rotating machine that converts mechanical power into electrical power. The relative motion between a magnetic field and a conductor creates an electrical current. The energy source harnessed to turn the generator varies widely. Most power stations in the world burn fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas to generate electricity. Others use nuclear power, but there is an increasing use of cleaner renewable sources such as solar, wind, wave and hydroelectric.
The world's first power station was designed and built by Lord Armstrong at Cragside, England in 1868. Water from one of the lakes was used to power Siemens dynamos. The electricity supplied power to lights, heating, produced hot water, ran an elevator as well as labor-saving devices and farm buildings.
The first public power station was the Edison Electric Light Station, built in London at 57, Holborn Viaduct, which started operation in January 1882. This was a project of Thomas Edison that was organized and managed by his partner, Edward Johnson. A Babcock & Wilcox boiler powered a 125-horsepower steam engine that drove a 27-ton generator called "Jumbo", after the celebrated elephant. This supplied electricity to premises in the area that could be reached through the culverts of the viaduct without digging up the road, which was the monopoly of the gas companies. The customers included the City Temple and the Old Bailey. Another important customer was the Telegraph Office of the General Post Office, but this could not be reached though the culverts. Johnson arranged for the supply cable to be run overhead, via Holborn Tavern and Newgate