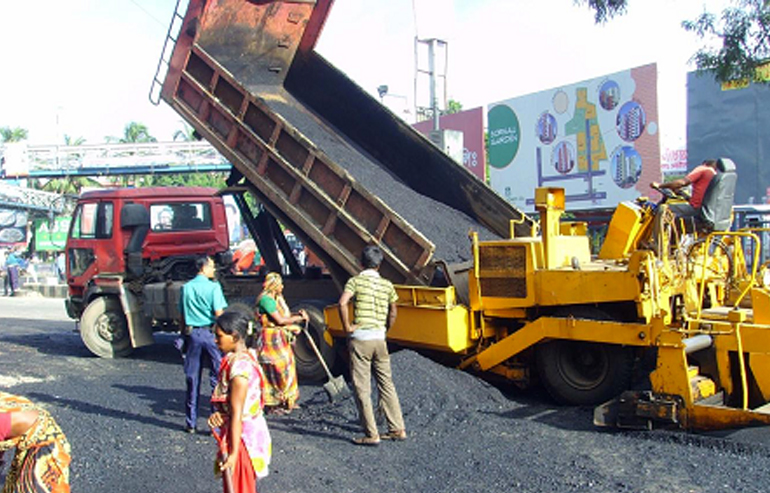
Paver Machine-01
Paver Machine-01
The asphalt is added from a dump truck or a material transfer unit into the paver's hopper. The conveyor then carries the asphalt from the hopper to the auger. The auger places a stockpile of material in front of the screed. The screed takes the stockpile of material and spreads it over the width of the road and provides initial compaction.
The paver should provide a smooth uniform surface behind the screed. In order to provide a smooth surface a free floating screed is used. It is towed at the end of a long arm which reduces the base topology effect on the final surface. The height of the screed is controlled by a number of factors including: the attack angle of the screed, weight and vibration of the screed, the material head and the towing force.
To conform to the elevation changes for the final grade of the road modern pavers use automatic screed controls, which generally control the screed's angle of attack from information gathered from a grade sensor. Additional controls are used to correct the slope, crown or superelevation of the finished pavement.